(Unmodified) Headless Chrome instrumented with Puppeteer: How consistent is the fingerprint in 2024?
In this article, we conduct a deep dive analysis of the fingerprint of an unmodified headless Chrome instrumented with Puppeteer browser. We compare it with the fingerprint of a normal Chrome browser used by a human user to identify the main differences and see if they can be leveraged for bot detection.
Note: This experiment was conducted in June 2024 on MacOS. The results may be different depending on your OS, the version of Chrome and Puppeteer used.
TL;DR
Unmodified Headless Chrome with Puppeteer exhibits a few fingerprint differences from a normal Chrome browser. In particular, it can be detected using:
navigator.webdriver = true
- The presence of the
HeadlessChromesubstring theuser-agentHTTP header
Fingerprint data collection
To collect a browser fingerprint, we create a script that
starts an unmodified Headless Chrome instrumented with Puppeteer. It visits the browser fingerprinting test
of deviceandbrowserinfo.com and saves the output
in the pptr-headless-chrome-vanila.json file.
const puppeteer = require('puppeteer');
const fs = require('fs');
(async () => {
const browser = await puppeteer.launch();
const page = await browser.newPage();
await page.goto('https://deviceandbrowserinfo.com/info_device');
await page.waitForFunction(() => {
return window.fingerprint && window.fingerprint.speechSynthesisVoices;
})
const fingerprint = await page.evaluate(() => {
return window.fingerprint;
});
fs.writeFileSync('./pptr-headless-chrome-vanila.json', JSON.stringify(fingerprint, null, 2));
await browser.close()
})();
The browser fingerprint of Headless Chrome instrumented with Puppeteer looks as follows:
{
"headers": [
{
"name": "Connection",
"value": "upgrade"
},
{
"name": "Host",
"value": "deviceandbrowserinfo.com"
},
{
"name": "X-Forwarded-For",
"value": "XXXXXXXX"
},
{
"name": "sec-ch-ua",
"value": "\"Chromium\";v=\"125\", \"Not.A/Brand\";v=\"24\""
},
{
"name": "sec-ch-ua-mobile",
"value": "?0"
},
{
"name": "sec-ch-ua-platform",
"value": "\"macOS\""
},
{
"name": "Upgrade-Insecure-Requests",
"value": "1"
},
{
"name": "User-Agent",
"value": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) HeadlessChrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
},
{
"name": "Accept",
"value": "text/html,application/xhtml+xml,application/xml;q=0.9,image/avif,image/webp,image/apng,*/*;q=0.8,application/signed-exchange;v=b3;q=0.7"
},
{
"name": "Sec-Fetch-Site",
"value": "none"
},
{
"name": "Sec-Fetch-Mode",
"value": "navigate"
},
{
"name": "Sec-Fetch-User",
"value": "?1"
},
{
"name": "Sec-Fetch-Dest",
"value": "document"
},
{
"name": "Accept-Encoding",
"value": "gzip, deflate, br, zstd"
},
{
"name": "Accept-Language",
"value": "en-GB,en-US;q=0.9,en;q=0.8"
}
],
"userAgent": "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) HeadlessChrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36",
"platform": "MacIntel",
"userAgentData": {},
"speechSynthesisVoices": {
"defaultVoice": {
"voiceURI": "Daniel (English (United Kingdom))",
"name": "Daniel (English (United Kingdom))",
"lang": "en-GB",
"localService": true,
"default": true
},
"numVoices": 157,
"numLocalServices": 157,
"numGoogleVoices": 0,
"hasRussianLocalVoice": true
},
"timezone": "Europe/Paris",
"localeLanguage": "en-GB",
"languages": [
"en-GB",
"en-US",
"en"
],
"hardwareConcurrency": 4,
"deviceMemory": 8,
"plugins": "PDF Viewer::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer:: - Chrome PDF Viewer::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer:: - Chromium PDF Viewer::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer:: - Microsoft Edge PDF Viewer::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer:: - WebKit built-in PDF::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer::",
"mimeTypes": [
"Portable Document Format~~application/pdf~~pdf",
"Portable Document Format~~text/pdf~~pdf"
],
"language": "en-GB",
"screenWidth": 2560,
"screenHeight": 1440,
"colorDepth": 24,
"availWidth": 2560,
"availHeight": 1440,
"maxTouchPoints": 0,
"hasAccelerometer": false,
"fonts": [
"Arial Unicode MS",
"Gill Sans",
"Helvetica Neue",
"Menlo",
"Univers CE 55 Medium"
],
"webGLVendor": "Google Inc. (Intel)",
"webGLRenderer": "ANGLE (Intel, ANGLE Metal Renderer: Intel(R) Iris(TM) Plus Graphics, Unspecified Version)",
"canvas": "data:image/png;base64,...",
"hasModifiedCanvasFingerprint": false,
"colorGamut": [
"srgb",
"any"
],
"anyPointer": [
"fine",
"any"
],
"anyHover": [
"hover",
"any"
],
"audioCodecs": {
"ogg": "probably",
"mp3": "probably",
"wav": "probably",
"m4a": "maybe",
"aac": "probably"
},
"videoCodecs": {
"ogg": "",
"h264": "probably",
"webm": "probably",
"mpeg4v": "",
"mpeg4a": "",
"theora": ""
},
"webdriver": true,
"cdpCheck1": true,
"callPhantom": false,
"_phantom": false,
"phantom": false,
"nightmare": false,
"sequentum": false,
"chromeObject": true,
"architecture": "x86",
"bitness": "64",
"model": "",
"platformVersion": "14.5.0",
"webGPUAdapterInfo": {
"vendor": "intel",
"architecture": "gen-11",
"device": "",
"description": ""
},
"audioFingerprint": {
"nt_vc_output": {
"ac-baseLatency": 0.005333333333333333,
"ac-outputLatency": 0,
"ac-sinkId": "",
"ac-sampleRate": 48000,
"ac-state": "suspended",
"ac-maxChannelCount": 2,
"ac-numberOfInputs": 1,
"ac-numberOfOutputs": 0,
"ac-channelCount": 2,
"ac-channelCountMode": "explicit",
"ac-channelInterpretation": "speakers",
"an-fftSize": 2048,
"an-frequencyBinCount": 1024,
"an-minDecibels": -100,
"an-maxDecibels": -30,
"an-smoothingTimeConstant": 0.8,
"an-numberOfInputs": 1,
"an-numberOfOutputs": 1,
"an-channelCount": 2,
"an-channelCountMode": "max",
"an-channelInterpretation": "speakers"
},
"pxi_output": 124.04347657808103
},
"GPUDeviceLimits": {
"maxTextureDimension1D": 8192,
"maxTextureDimension2D": 8192,
"maxTextureDimension3D": 2048,
"maxTextureArrayLayers": 256,
"maxBindGroups": 4,
"maxBindGroupsPlusVertexBuffers": 24,
"maxBindingsPerBindGroup": 1000,
"maxDynamicUniformBuffersPerPipelineLayout": 8,
"maxDynamicStorageBuffersPerPipelineLayout": 4,
"maxSampledTexturesPerShaderStage": 16,
"maxSamplersPerShaderStage": 16,
"maxStorageBuffersPerShaderStage": 8,
"maxStorageTexturesPerShaderStage": 4,
"maxUniformBuffersPerShaderStage": 12,
"maxUniformBufferBindingSize": 65536,
"maxStorageBufferBindingSize": 134217728,
"minUniformBufferOffsetAlignment": 256,
"minStorageBufferOffsetAlignment": 256,
"maxVertexBuffers": 8,
"maxBufferSize": 268435456,
"maxVertexAttributes": 16,
"maxVertexBufferArrayStride": 2048,
"maxInterStageShaderComponents": 60,
"maxInterStageShaderVariables": 16,
"maxColorAttachments": 8,
"maxColorAttachmentBytesPerSample": 32,
"maxComputeWorkgroupStorageSize": 16384,
"maxComputeInvocationsPerWorkgroup": 256,
"maxComputeWorkgroupSizeX": 256,
"maxComputeWorkgroupSizeY": 256,
"maxComputeWorkgroupSizeZ": 64,
"maxComputeWorkgroupsPerDimension": 65535
},
"speakers": 1,
"micros": 1,
"webcams": 1,
"seleniumChromeDefault": false,
"areYouBotPage": false,
"jsHash1": "204b2949dc42d6c80854083460497653b703d81c702c3f45e7301ddd48d6c579"
}
To collect the normal (human) Chrome browser fingerprint,
we visit the same page manually in a Chrome browser and open the dev tools after the JS fingerprint script
has been executed to avoid any potential side effects. Then, we copy the fingerprint by typing the following
command copy(JSON.stringify(window.fingerprint, null, 2)) and save the output of the human
Chrome fingerprint in a file named human-chrome.json .
To compare the two browser fingerprints, we use the json-diff package. We store the output in
diffpptr-vanila-vs-human-chrome.diff
json-diff pptr-headless-chrome-vanila.json human-chrome.json > diffpptr-vanila-vs-human-chrome.diff
The fingerprint diff looks as follows. The value with a
- corresponds to the fingerprint of Headless Chrome instrumented with Puppeteer while the
values with a + are linked to the human Chrome. Note that we truncated the values of the canvas
fingerprint for readability purposes, but the values are different between are normal Chrome and a Headless
Chrome with Puppeteer (we discuss it more in detail later in this article).
{
headers: [
...
...
...
{
- value: "\"Chromium\";v=\"125\", \"Not.A/Brand\";v=\"24\""
+ value: "\"Google Chrome\";v=\"125\", \"Chromium\";v=\"125\", \"Not.A/Brand\";v=\"24\""
}
...
...
+ {
+ name: "sec-ch-ua-form-factors"
+ value: "\"Desktop\""
+ }
...
{
- value: "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) HeadlessChrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
+ value: "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
}
...
...
...
...
...
...
{
- value: "en-GB,en-US;q=0.9,en;q=0.8"
+ value: "en,fr-FR;q=0.9,fr;q=0.8,en-US;q=0.7"
}
]
- userAgent: "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) HeadlessChrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
+ userAgent: "Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) Chrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36"
userAgentData: {
+ brands: [
+ {
+ brand: "Google Chrome"
+ version: "125"
+ }
+ {
+ brand: "Chromium"
+ version: "125"
+ }
+ {
+ brand: "Not.A/Brand"
+ version: "24"
+ }
+ ]
+ mobile: false
+ platform: "macOS"
}
speechSynthesisVoices: {
- numVoices: 157
+ numVoices: 176
- numGoogleVoices: 0
+ numGoogleVoices: 19
}
languages: [
- "en-GB"
+ "en"
+ "fr-FR"
+ "fr"
...
- "en"
]
- language: "en-GB"
+ language: "en"
- availHeight: 1440
+ availHeight: 1415
- webGLVendor: "Google Inc. (Intel)"
+ webGLVendor: "Google Inc. (Intel Inc.)"
- webGLRenderer: "ANGLE (Intel, ANGLE Metal Renderer: Intel(R) Iris(TM) Plus Graphics, Unspecified Version)"
+ webGLRenderer: "ANGLE (Intel Inc., Intel(R) Iris(TM) Plus Graphics OpenGL Engine, OpenGL 4.1)"
- canvas: "data:image/png;base64, ... value 1"
+ canvas: "data:image/png;base64, ... value 2"
- webdriver: true
+ webdriver: false
- jsHash1: "204b2949dc42d6c80854083460497653b703d81c702c3f45e7301ddd48d6c579"
+ jsHash1: "a4d9d8f25e90fdfc2f01cc0f350d84a3a425a58147ec5126664814d0c7928cf6"
}
What are the main differences between an unmodified Headless Chrome instrumented with Puppeteer and a normal (human) Chrome browser?
The first difference we observe is that by default,
Headless Chrome still has a discriminating user agent:
Mozilla/5.0 (Macintosh; Intel Mac OS X 10_15_7) AppleWebKit/537.36 (KHTML, like Gecko) HeadlessChrome/125.0.0.0 Safari/537.36 It
contains the HeadlessChrome substring that makes it easy to detect using only server-side
signals.
We also observe that by default, Puppeteer with headless Chrome relies on Chromium and not Chrome, as indicated in some of the client hints HTTP headers:
{
- value: "\"Chromium\";v=\"125\", \"Not.A/Brand\";v=\"24\""
+ value: "\"Google Chrome\";v=\"125\", \"Chromium\";v=\"125\", \"Not.A/Brand\";v=\"24\""
}
We also notice the absence of the
userAgentData field collected using navigator.userAgentData by default in Headless
Chrome.
Navigator.webdriver = true
Besides the user agent, one of the most discriminating
differences is the fact that navigator.webdriver is set to true when Headless
Chrome is instrumented with Puppeteer.
WebGL fingerprinting differences
Attributes related to the GPU collected using the WebGL APIs are also different between a normal Chrome and headless chrome with Puppeteer:
- webGLVendor: "Google Inc. (Intel)"
+ webGLVendor: "Google Inc. (Intel Inc.)"
- webGLRenderer: "ANGLE (Intel, ANGLE Metal Renderer: Intel(R) Iris(TM) Plus Graphics, Unspecified Version)"
+ webGLRenderer: "ANGLE (Intel Inc., Intel(R) Iris(TM) Plus Graphics OpenGL Engine, OpenGL 4.1)"
Language differences
We also observe several differences related to the languages. The most significant difference is linked to the speech synthesis API:
speechSynthesisVoices: {
- numVoices: 157
+ numVoices: 176
- numGoogleVoices: 0
+ numGoogleVoices: 19
}
Headless Chrome instrumented with Puppeteer has 157 voices vs 176 for a normal Chrome. This difference is caused by the absence of Google voices in Headless Chrome, certainly due to the fact that Puppeteer relies on Chromium and not the real Chrome as discussed previously.
We also observe differences in the user-preferred
languages collected using navigator.languages and in the accept-language HTTP
headers. However, these differences are not really relevant as they are more linked to the user preferences
than the browser itself and can easily be modified.
Screen height differences
We observe a slight difference in terms of screen
resolution when collecting the available height of the screen using the screen.availHeight :
1440 pixels for headless chrome vs 1415 for the normal Chrome. Note that this
difference is not something absolute and has to be interpreted with regard to other screen-related
attributes
Canvas fingerprinting differences
The two browsers have different canvas fingerprints. Headless Chrome with Puppeteer has the following canvas fingerprint:

While the normal Chrome (human) has the following canvas fingerprint:

Visually, it’s difficult to detect any differences between the two canvases. Thus, we compute the difference of the two canvas fingerprints using the following python code and store the difference as an image.
from PIL import Image, ImageChops
def image_diff(image1_path, image2_path, output_path):
# Open the two images
image1 = Image.open(image1_path)
image2 = Image.open(image2_path)
# Ensure both images have the same size
if image1.size != image2.size:
raise ValueError("Images must have the same dimensions")
# Compute the difference between the images
diff = ImageChops.difference(image1, image2)
# Save the result
diff.save(output_path)
print(f"Difference image saved to {output_path}")
# Example usage
puppeteer_canvas_path = './pptr-canvas.png'
human_canvas_path = './human-canvas.png'
diff_output_path = 'diff_canvas.png'
image_diff(puppeteer_canvas_path, human_canvas_path, diff_output_path)
The difference is subtle (cf image below). We observe a few dots that located close to the border of the circles drawn in the canvas fingerprinting challenge.
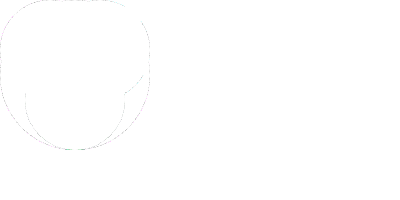
Fingerprinting differences that don’t exist anymore
In previous articles published in 2017 and 2018, I
presented certain techniques to detect Headless Chrome, such as the absence of plugins (with
navigator.plugins ), the absence of the window.chrome object and the absence of
navigator.languages .
If we look at the Headless Chrome fingerprint above, we observe that as of June 2024, an unmodified Headless Chrome instrumented with Puppeteer doesn’t exhibit these inconsistencies anymore. By default, it has:
- A correct list of plugins in
navigator.plugins:"PDF Viewer::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer:: - Chrome PDF Viewer::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer:: - Chromium PDF Viewer::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer:: - Microsoft Edge PDF Viewer::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer:: - WebKit built-in PDF::Portable Document Format::internal-pdf-viewer::"
- A
window.chromeobject defined
- A correct list of preferred languages in
navigator.languagesdefined:["en-GB", "en-US", "en"]
Thus, the surface of detection has decreased over time, which makes the detection of instrumented headless Chrome more difficult. This is caused by the fact that Headless Chrome had a significant update in 2023 that merged the code of Headless Chrome with the code of the normal Chrome.
Conclusion
In this article, we studied the main browser
fingerprinting differences between a normal Chrome browser and a Headless Chrome browser instrumented with
Puppeteer. We detected a few differences such as navigator.webdriver = true and a
discriminating user agent that makes it easy to detect unmodified Headless Chrome browsers.
We also observed other changes that are caused by the fact
that by default, Puppeteer leverages a Chromium browser instead of a real Chrome browser, for example, the
absence of Google-related languages with the speechSynthesis.getVoices() API.
However, these are fingerprinting differences that can be easily modified by an attacker:
- An attacker can use a real (headless) Chrome browser instead of the Chromium browser bundled with Puppeteer;
- They can easily change their user-agent using the Puppeteer
page.setUserAgent()method.
- They can get rid of
navigator.webdriverby creating a browser withargs: ['--disable-blink-features=AutomationControlled']